Following topics are covered –
- JVM
- Overall-view picture
- Summery of different parts
- Internals Architecture of JVM
- JIT
- Garbage Collection
- Types of JVM GC
- FAQs
- What are the different sections of Heap and how the different sections are cleared?(Barclays)
- GC ALgo
- JVM config
- JVMHeap Dump
- JMM -Java Memory map
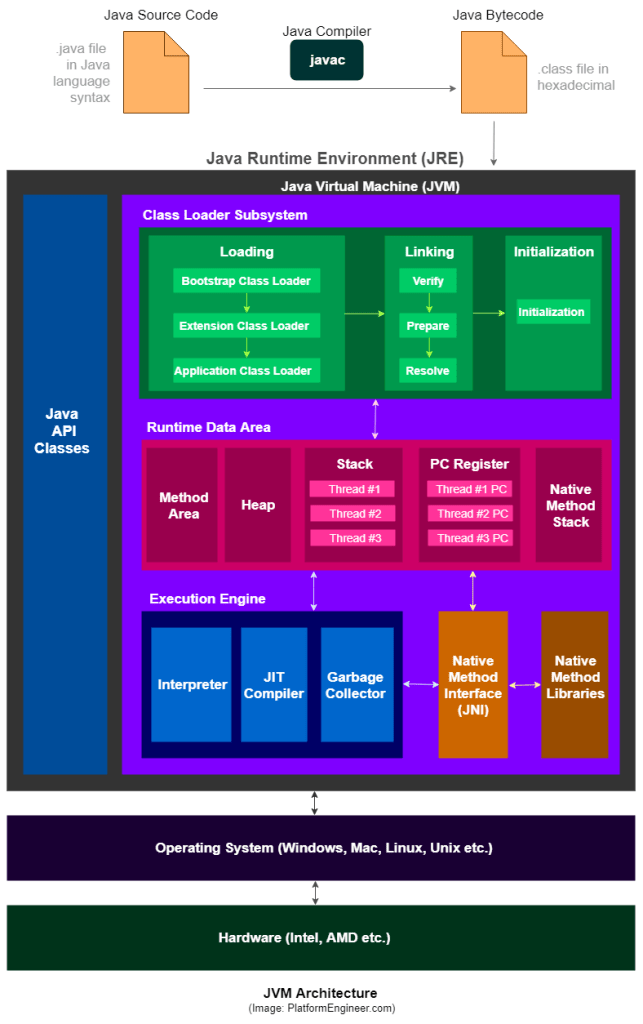
JVM’s Job –Load & Execute
JVM has various sub components internally.
- Class loader sub system: JVM’s class loader sub system performs 3 tasks
a. It loads .class file into memory.
b. It verifies byte code instructions.
c. It allots memory required for the program. - Run time data area: This is the memory resource used by JVM and it is divided into 5 parts
a. Method area: Method area stores class code and method code. (metaspace in Java SE 8)
b. Heap: Objects are created on heap.
c. Java stacks: Java stacks are the places where the Java methods are executed. A Java stack contains frames. On each frame, a separate method is executed.
d. Program counter registers: The program counter registers store memory address of the instruction to be executed by the micro processor.
e. Native method stacks: The native method stacks are places where native methods (for example, C language programs) are executed. Native method is a function, which is written in another language other than Java. - Native method interface: Native method interface is a program that connects native methods libraries (C header files) with JVM for executing native methods.
- Native method library: holds the native libraries information.
- Execution engine: Execution engine contains interpreter and JIT compiler, which converts byte code into machine code. JVM uses optimization technique(Hotspot Profiler) to decide which part to be interpreted and which part to be used with JIT compiler. The HotSpot represent the block of code(frequent) executed by JIT compiler.