Objective –
- meaning /structure of security mechanism
- where used? use case
- Implementation
Index
- Introduction
- Basic username-pwd
- JWT
- Oauth ( micro-services)
- Digital Signature (NPCI)
Introduction
Session, Cookie, JWT, Token, SSO, and OAuth 2.0 – here’s what you need to know
These terms are essential for identifying, authenticating, and authorizing users online. Let’s dive in👇
𝗪𝗪𝗪-𝗔𝘂𝘁𝗵𝗲𝗻𝘁𝗶𝗰𝗮𝘁𝗲
🔹 Oldest & most basic method
🔹 Browser asks for username & password
🔹 Lacks control over login life cycle
🔹 Rarely used today
𝗦𝗲𝘀𝘀𝗶𝗼𝗻-𝗖𝗼𝗼𝗸𝗶𝗲
🔹 Server maintains session storage
🔹 Browser keeps session ID
🔹 Works mainly with browsers, not mobile app friendly
𝗧𝗼𝗸𝗲𝗻
🔹 Compatible with mobile apps
🔹 Client sends token to server for validation
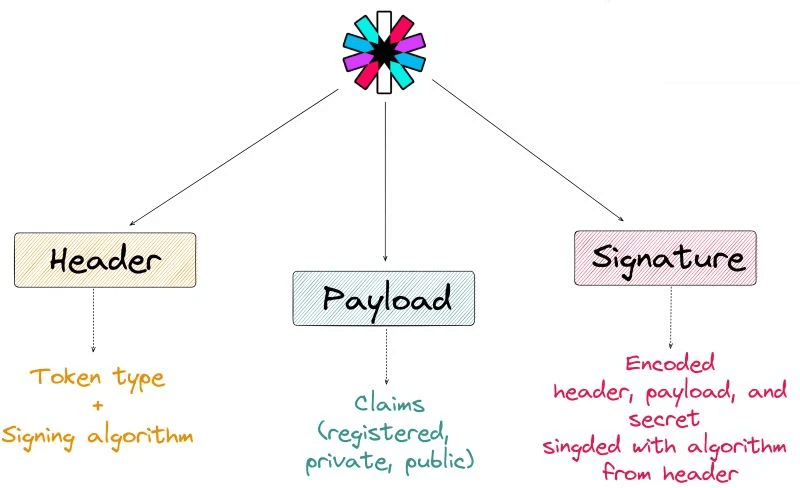
𝗝𝗪𝗧 (𝗝𝗦𝗢𝗡 𝗪𝗲𝗯 𝗧𝗼𝗸𝗲𝗻)
🔹 Standard representation of tokens
🔹 Digitally signed & verifiable
🔹 No need to save session info server-side
𝗦𝗦𝗢 (𝗦𝗶𝗻𝗴𝗹𝗲 𝗦𝗶𝗴𝗻-𝗢𝗻) & 𝗢𝗔𝘂𝘁𝗵 𝟮.𝟬
🔹 SSO: Log in once, access multiple sites
🔹 Uses CAS (central authentication service)
🔹 OAuth 2.0: Authorize one site to access info on another