Introduction
Index
- Definition
- Why Spring Needed?
- Spring Modules
- IOC and DI
- Introduction
- Differences
Definition –
- Spring is an open source framework since February 2003.
- Allows us to give capability of EJBs to plain JavaBeans without using an application server.
- Spring is a lightweight , dependency injection and aspect-oriented container and framework. works on IOC(Inversion of control)
- Lightweight Lesser no of JARs – JavaBeans / POJOs in Spring-enabled application often have no dependencies on Spring-specific classes.
- Dependency Injection Spring allows loose coupling through dependency injection (DI).
- DI =instead of an object looking up dependencies from a container(in EJB from EJB container or in RMI from RMIRegistry) or creating its own dependency(in Fixed JDBC , conn = DM.getCn(….)) , the container gives the dependencies to the object at instantiation without waiting to be asked.
- You can think of D.I as JNDI(Java naming & directory iterface — Naming service) in reverse.
- Aspect-oriented Spring supports aspect-oriented programming(AOP)
- (AOP) allows separating application business logic from system services (such as auditing and transaction management,logging , security,transactions). Application objects perform only business logic and nothing more.
- Why Spring is a Container ?
- Spring is a container which manages the life-cycle and configuration of application objects.(spring beans) In Spring, using config XMLs or annotations or java config, you can declare –
- how to create each of your application objects(spring beans)
- how to configure them
- how they should be associated with each other.(collaboration/wiring/coupling=connecting dependencies with dependent objs)
- Spring is a container which manages the life-cycle and configuration of application objects.(spring beans) In Spring, using config XMLs or annotations or java config, you can declare –
- Why Spring is a framework ?
- Spring allows you to configure and compose complex applications from simpler components. In Spring, application objects are composed declaratively, typically in an XML file or using annotations.
- Spring also provides you with ready made implemetations of services like – transaction management, persistence framework,web mvc etc.

Why learn one more framework — when you already have EJB,Struts,Hibernate etc….
- Build applications from plain old Java objects (POJOs) (known as spring beans )
- Apply enterprise services non-invasively.
- (w/o invasion means — POJOs DONT implement or extend from spring APIs) This capability applies to the Java SE programming model and to full and partial Java EE.
- Example of how you, as an application developer, can use the Spring platform advantage:
- Make a Java method execute in a database transaction without having to deal with transaction APIs.
- Make a local Java method a remote procedure without having to deal with remote APIs.
- Make a local Java method an ORM operation without having to deal with overheads of ORM set up.
Why Spring needed? (in Simple terms – generic term & 4 key points of why spring)
To simplify Java development.
- lightweight & min intrusive(POJOs not tied to spring) development with POJOs
- Loose coupling thro’ DI/IoC & with usage of i/f
- Declarative prog(XML or anno or java config) + thro’ Aspects & common conventions
- Boilerplate code reduction thro aspects & templates.
Spring framework Modules
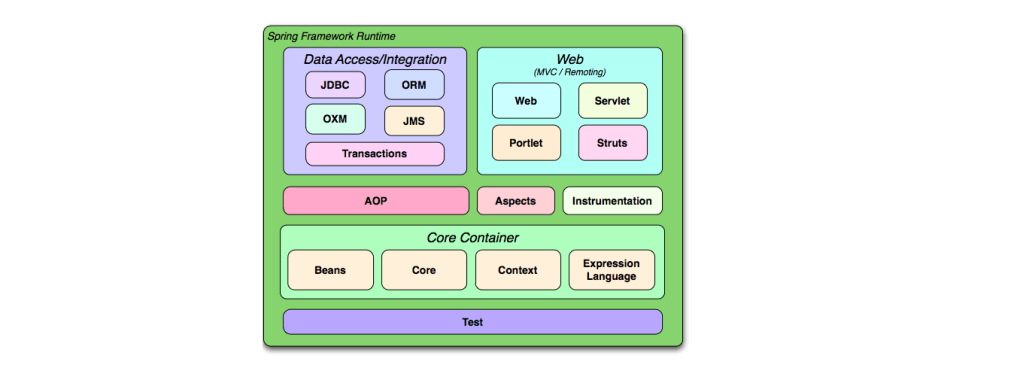
- Core Container
- beans
- Core
- Context
- Expression Language
- Web
- Web
- Serlvlet
- Portlet
- Struts
- Data Access/Integration
- ORM
- JMS
- JDBC
- Transactions
- AOP
- Test
IOC And DI
- The org.springframework.beans and org.springframework.context packages are the basis for Spring Framework’s IoC container.
IOC- Inversion of Control
- Inversion of Control Rather a generic term, (IoC) is an object-oriented programming practice where the object coupling(dependent obj bound with dependency) is bound at run time by an assembler object(eg spring container) and is typically not known at compile time using static analysis.
- Unlike in traditional programs — where dependent obj creates dependencies leading to tight coupling , container sets the dependencies (not US –not a prog or not a dependent obj) —so its inversion of control
Inversion of Control is sometimes referred to as the “Hollywood Principle: Don’t call us, we’ll call you”,
Why IoC or Dependency Injection (advantages of IoC)
- There is a decoupling of the execution of a certain task from implementation.
- Every module can focus on what it is designed for.
- Modules make no assumptions about what other systems do but rely on their contracts/specs (=i/f)
- Replacing modules has no side effect on other modules.
Dependency injection (DI)
- (DI) is the ability to inject dependencies. DI can help make your code architecturally pure. It aids in using a design by interface approach as well as test driven development by providing a consistent way to inject dependencies.
- For example :
- a data access object (DAO) may need a database connection. Thus the DAO depends on the database connection. Instead of looking up the database connection with JNDI, you could inject it.
- or another eg is JMS — conn factory or destination
- For example :
