9.Deploying and Managing Infrastructure at Scale Section
Index
- Cloud formation
- cdk
- EBS
- CodeDeploy
- CodeCommit
- CodeBuild
- CodePipeline
- CodeArtifact
- CodeStar
- Cloud9
- aws System manager
- opsWork -chef Puppet
What is CloudFormation
CloudFormation is a declarative way of outlining your AWS
Infrastructure, for any resources (most of them are supported).
CloudFormation creates resources as declared for you, in the right order, with the
exact configuration that you specify
Benefits of AWS CloudFormation
- Infrastructure as code
- No resources are manually created, which is excellent for control
- Changes to the infrastructure are reviewed through code
- Cost –
- Each resources within the stack is tagged with an identifier so you can easily see how much a stack costs you
- You can estimate the costs of your resources using the CloudFormation template
- Savings strategy: In Dev, you could automation deletion of templates at 5 PM and recreated at 8 AM, safely
- Productivity
- Ability to destroy and re-create an infrastructure on the cloud on the fly
- Declarative programming (no need to figure out ordering and orchestration
- Don’t re-invent the wheel
- Leverage existing templates on the web!
- Supports (almost) all AWS resources
- Everything we’ll see in this course is supported
- You can use “custom resources” for resources that are not supported
AWS Cloud Development Kit (CDK)
Define your cloud infrastructure using a familiar language
The code is “compiled” into a CloudFormation template (JSON/YAML)
• You can therefore deploy infrastructure and application runtime code together
Developer problems on AWS
• Managing infrastructure
• Deploying Code
• Configuring all the databases, load balancers, etc
• Scaling concerns
- Most web apps have the same architecture (ALB + ASG)
- All the developers want is for their code to run!
- Possibly, consistently across different applications and environments
Solution – EBS!
AWS Elastic Beanstalk Overview
Elastic Beanstalk is a developer centric view of deploying an application on AWS
It uses all the component’s we’ve seen before: EC2, ASG, ELB, RDS, etc…
We still have full control over the configuration
Beanstalk = Platform as a Service (PaaS)
Beanstalk is free but you pay for the underlying instances
Elastic Beanstalk
Managed service
• Instance configuration / OS is handled by Beanstalk
• Deployment strategy is configurable but performed by Elastic Beanstalk
• Capacity provisioning
• Load balancing & auto-scaling
• Application health-monitoring & responsiveness
Just the application code is the responsibility of the developer
Three architecture models:
• Single Instance deployment: good for dev
• LB + ASG: great for production or pre-production web applications
• ASG only: great for non-web apps in production (workers, etc..)
Elastic Beanstalk – Health Monitoring
Health agent pushes metrics to CloudWatch
AWS CodeDeploy [alternative of GitHub action]
We want to deploy our application automatically
• Works with EC2 Instances
• Works with On-Premises Servers
• Hybrid service
Servers / Instances must be provisioned and configured ahead of time with the CodeDeploy Agent
AWS CodeCommit [Alternative of guthub ]
Before pushing the application code to servers, it needs to be stored
somewhere
• Developers usually store code in a repository, using the Git technology
• A famous public offering is GitHub, AWS’ competing product is CodeCommit
Benefits:
• Fully managed
• Scalable & highly available
• Private, Secured, Integrated with AWS
AWS CodeBuild
Code building service in the cloud (name is obvious)
• Compiles source code, run tests, and produces packages that are ready to be
deployed (by CodeDeploy for example)
Benefits:
• Fully managed, serverless
• Continuously scalable & highly available
• Secure
• Pay-as-you-go pricing – only pay for the build time
AWS CodePipeline
Orchestrate the different steps to have the code automatically pushed to production
• Code => Build => Test => Provision => Deploy
• Basis for CICD (Continuous Integration & Continuous Delivery)
• Benefits:
• Fully managed, compatible with CodeCommit, CodeBuild, CodeDeploy, Elastic Beanstalk,
CloudFormation, GitHub, 3rd-party services (GitHub…) & custom plugins…
• Fast delivery & rapid updates

AWS CodeArtifact [similar to maven]
• Software packages depend on each other to be built (also called code
dependencies), and new ones are created
• Storing and retrieving these dependencies is called artifact management
• Traditionally you need to setup your own artifact management system
• CodeArtifact is a secure, scalable, and cost-effective artifact
management for software development
• Works with common dependency management tools such as Maven,
Gradle, npm, yarn, twine, pip, and NuGet
• Developers and CodeBuild can then retrieve dependencies straight
from CodeArtifact
AWS CodeStar
• Unified UI to easily manage software development activities in one place
• “Quick way” to get started to correctly set-up CodeCommit, CodePipeline,
CodeBuild, CodeDeploy, Elastic Beanstalk, EC2, etc…
• Can edit the code ”in-the-cloud” using AWS Cloud9
AWS Cloud9
AWS Cloud9 is a cloud IDE
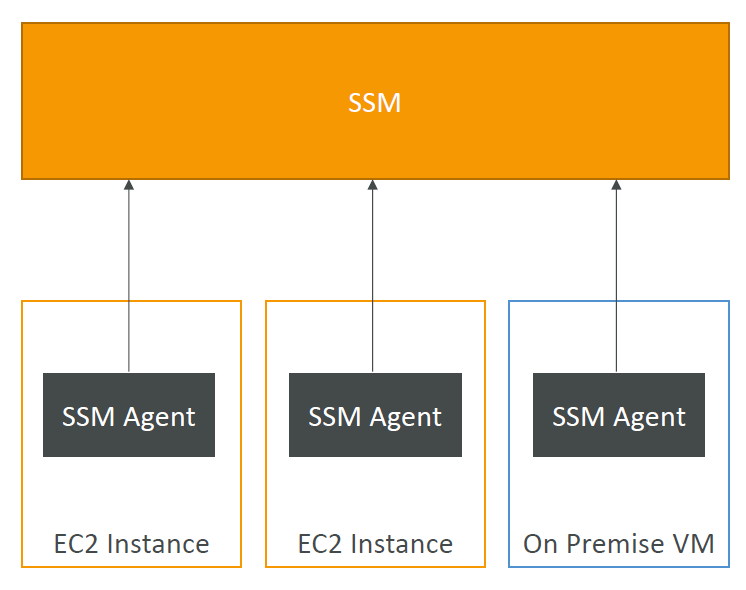
AWS Systems Manager (SSM)
- Helps you manage your EC2 and On-Premises systems at scale
- Another Hybrid AWS service
- Get operational insights about the state of your infrastructure
- Suite of 10+ products
- Most important features are:
- Patching automation for enhanced compliance
- Run commands across an entire fleet of servers
- Store parameter configuration with the SSM Parameter Store
- Works for both Windows and Linux OS
How Systems Manager works
We need to install the SSM agent onto the systems we control
• Installed by default on Amazon Linux AMI & some Ubuntu AMI
• If an instance can’t be controlled with SSM, it’s probably an issue with the SSM agent!
• Thanks to the SSM agent, we can run commands, patch & configure our servers
AWS OpsWorks
Chef & Puppet help you perform server configuration automatically, or repetitive actions
• They work great with EC2 & On-Premises VM
• AWS OpsWorks = Managed Chef & Puppet
• It’s an alternative to AWS SSM
• Only provision standard AWS resources:
• EC2 Instances, Databases, Load Balancers, EBS volumes…
In the exam: Chef or Puppet needed => AWS OpsWorks
Deployment – Summary
• CloudFormation: (AWS only)
• Infrastructure as Code, works with almost all of AWS resources
• Repeat across Regions & Accounts
• Beanstalk: (AWS only)
• Platform as a Service (PaaS), limited to certain programming languages or Docker
• Deploy code consistently with a known architecture: ex, ALB + EC2 + RDS
• CodeDeploy (hybrid): deploy & upgrade any application onto servers
• Systems Manager (hybrid): patch, configure and run commands at scale
• OpsWorks (hybrid): managed Chef and Puppet in AWS