10.Global Infrastructure Section
Why make a global application?
- • A global application is an application deployed in multiple geographies
- • On AWS: this could be Regions and / or Edge Locations
- • Decreased Latency
- • Latency is the time it takes for a network packet to reach a server
- • It takes time for a packet from Asia to reach the US
- • Deploy your applications closer to your users to decrease latency, better experience
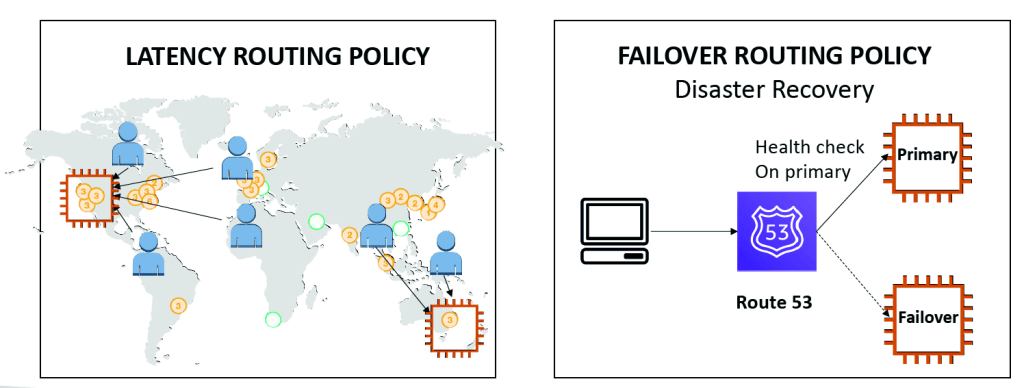
- • Disaster Recovery (DR)
- • If an AWS region goes down (earthquake, storms, power shutdown, politics)…
- • You can fail-over to another region and have your application still working
- • A DR plan is important to increase the availability of your application
- • Attack protection: distributed global infrastructure is harder to attack
Amazon Route 53 Overview
• Route53 is a Managed DNS (Domain Name System)
• DNS is a collection of rules and records which helps clients understand
how to reach a server through URLs.
- • In AWS, the most common records are:
- • http://www.google.com => 12.34.56.78 == A record (IPv4)
- • http://www.google.com => 2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334 == AAAA IPv6
- • search.google.com => http://www.google.com == CNAME: hostname to hostname
- • example.com => AWS resource == Alias (ex: ELB, CloudFront, S3, RDS, etc…)
Route 53 Routing Policies
Need to know them at a high-level for the Cloud Practitioner Exam

AWS Cloud-front
- Content Delivery Network (CDN)
- Improves read performance, content is cached at the edge
- Improves users experience
- 216 Point of Presence globally (edge locations)
- DDoS protection (because worldwide), integration with Shield, AWS Web Application Firewall
CloudFront – Origins
- S3 bucket
- For distributing files and caching them at the edge
- Enhanced security with CloudFront Origin Access Identity (OAI)
- CloudFront can be used as an ingress (to upload files to S3)
- Custom Origin (HTTP)
- Application Load Balancer
- EC2 instance
- S3 website (must first enable the bucket as a static S3 website)
- Any HTTP backend you want
CloudFront vs S3 Cross Region Replication
- CloudFront:
- Global Edge network
- Files are cached for a TTL (maybe a day)
- Great for static content that must be available everywhere
S3 Cross Region Replication:
- Must be setup for each region you want replication to happen
- Files are updated in near real-time
- Read only
- Great for dynamic content that needs to be available at low-latency in few regions
S3 Transfer Acceleration
Increase transfer speed by transferring file to an AWS edge location which will forward the data to the S3 bucket in the target region
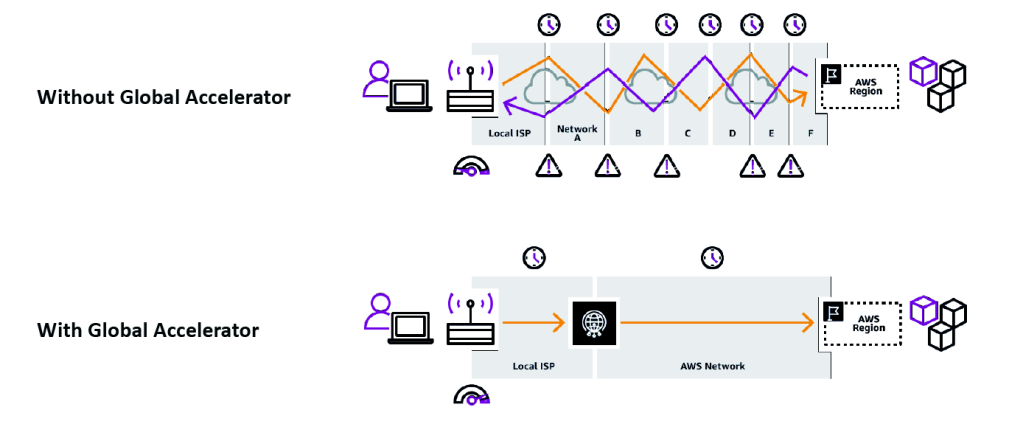
AWS Global Accelerator
• Improve global application availability and performance using the AWS global network
• Leverage the AWS internal network to optimize the route to your
application (60% improvement)
• 2 Anycast IP are created for your application and traffic is sent through
Edge Locations
• The Edge locations send the traffic to your application

AWS Global Accelerator vs CloudFront
- They both use the AWS global network and its edge locations around the world
- Both services integrate with AWS Shield for DDoS protection.
- CloudFront – Content Delivery Network
- Improves performance for your cacheable content (such as images and videos)
- Content is served at the edge
- Global Accelerator
- No caching, proxying packets at the edge to applications running in one or more AWS Regions.
- Improves performance for a wide range of applications over TCP or UDP
- Good for HTTP use cases that require static IP addresses
- Good for HTTP use cases that required deterministic, fast regional failover
AWS Outposts
- Benefits:
- • Low-latency access to on-premises systems
- • Local data processing
- • Data residency
- • Easier migration from on-premises to the cloud
- • Fully managed service
• Some services that work on Outposts: EC2 EBS S3 EKS etc
AWS WaveLength
- WaveLength Zones are infrastructure deploymentsembedded within the telecommunications providers’ datacenters at the edge of the 5G networks
- • Brings AWS services to the edge of the 5G networks
- • Example: EC2, EBS, VPC…
Summary
- Global DNS: Route 53
- • Great to route users to the closest deployment with least latency
- • Great for disaster recovery strategies
- • Global Content Delivery Network (CDN): CloudFront
- • Replicate part of your application to AWS Edge Locations – decrease latency
- • Cache common requests – improved user experience and decreased latency
- • S3 Transfer Acceleration
- • Accelerate global uploads & downloads into Amazon S3
- • AWS Global Accelerator:
- • Improve global application availability and performance using the AWS global network
- • AWS Outposts:
- • Deploy Outposts Racks in your own Data Centers to extend AWS services
- • AWS WaveLength:
- • Brings AWS services to the edge of the 5G networks
- • Ultra-low latency applications