1.Introduction
Traditional IT Overview
IT infrastructure consists of following aspects:
- Compute – CPU + RAM(Fast and temporary storage)
- Storage Data-(Long term storage e.g files)
- Database: store data in structured way
- Network – Router ,Switch,DNS server
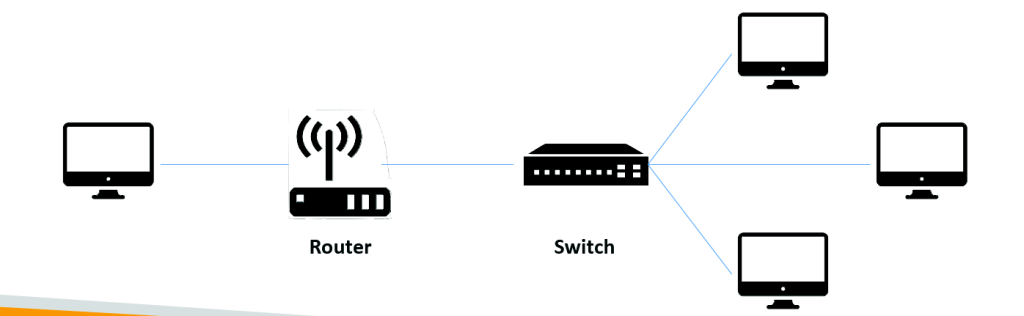
Networking terminologies:
- Network: Represents Cables, routers and servers connected with each other
- Router: A networking device that forwards data packets between computer networks. They know where to send your packets on the internet.. Its kind of intermediate connector.
- Switch: Takes a packet and send it to the correct server / client on your network. Its kind of Last mile connector.
Problems with Traditional IT Approach
- Pay for the rent for the data center
- Pay for power supply, cooling, maintenance
- Adding and replacing hardware takes time
- Scaling is limited (if organization becomes 10 times bigger you have to add on 10X infra , you MIGHT not have time or space to do so)
- Hire specialized 24/7 team to monitor the infrastructure
- How to deal with disasters? (earthquake, power shutdown, fire…)
Can we externalize all this? – Cloud
In AWS above functionality are provided by different services :
- Compute -EC2 , Lambda
- Storage – S3
- Database- RDS
- Network – VPC , Route 53
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing is the on-demand (You get when you need) delivery of compute power, database storage, applications, and other IT resources
Example of cloud service in day to day use – gmail , dropbox , Netflix – video streaming org build completely on aws.
Deployment Models in cloud :
| Private | Public* | Hybrid* |
|---|---|---|
| Cloud services used by a single organization, not exposed to the public. | Cloud resources owned and operated by a thirdparty cloud service provider delivered over the Internet. | Keep some servers on premises and extend some capabilities to the Cloud |
| Have Complete control | Six Advantages of Cloud Computing | Control over sensitive assets in your private infrastructure |
| Security for sensitive applications | Flexibility and cost-effectiveness of the public cloud | |
| Meet specific business needs | ||
| Example : Rackspace | Example : aws , Azure,GCP |
Six Advantages of Cloud Computing (Abbr- Trade – massive economies – Stop guessing -spending-Increased speed – go global in mins)
- Trade capital expense (CAPEX) for operational expense (OPEX)
- Trade capital expense for variable expense
- Pay On-Demand: don’t own hardware
- Reduced Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) & Operational Expense (OPEX)
- Benefit from massive economies of scale
- Prices are reduced as AWS is more efficient due to large scale
- Stop guessing capacity
- No need to plan services and infra in advance and at runtime expect capacity to meet demand .
- Scale based on actual measured usage
- Stop spending money running and maintaining data centers
- Increased Speed and Agility
- Go global in minutes
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/whitepapers/latest/aws-overview/six-advantages-of-cloud-computing.html
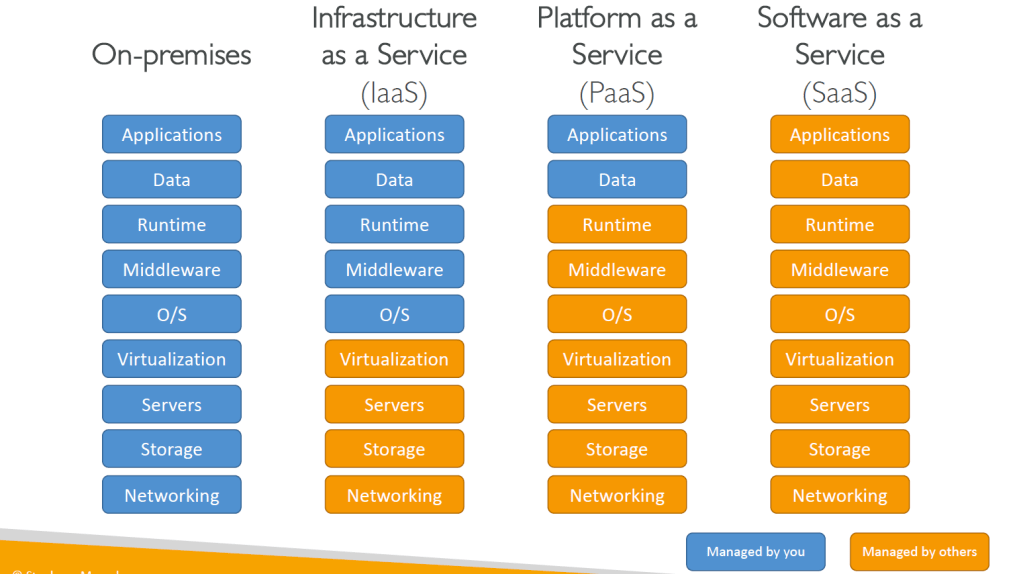
Types of Cloud Computing:
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
- Provide building blocks for cloud IT
- Provides networking, computers, data storage space
- Highest level of flexibility
- Easy parallel with traditional on-premises IT
- Hardware/resources provided we manage it
- Platform as a Service (PaaS)
- Removes the need for your organization to manage the underlying infrastructure
- Focus on the deployment and management of your applications
- Software as a Service (SaaS)
- Completed product that is run and managed by the service provider
Cloud Composed of following Functionality
Example of Cloud Computing Types
- Infrastructure as a Service:
- Amazon EC2 (on AWS)
- GCP, Azure, Rackspace, Digital Ocean, Linode
- Platform as a Service
- Elastic Beanstalk (on AWS)
- Heroku, Google App Engine (GCP), Windows Azure (Microsoft)
- Software as a Service:
- Many AWS services (ex: Rekognition for Machine Learning)
- Google Apps (Gmail), Dropbox, Zoom
Pricing of the Cloud – Quick Overview
AWS has 3 pricing fundamentals, following the pay-as-you-go pricing
model
- Compute:
- Pay for compute time
- Storage
- Pay for data stored in the Cloud
- Data transfer OUT of the Cloud(Networking)
- Data transfer IN is free
AWS Global Infrastructure
AWS Region– cluster of data centers, it is a geographical region. Services are region scoped
How do you choose an aws region?
It depends on following criteria
- Compliance with data governance and legal requirements: data never leaves a region without your explicit permission.
- Latency – Proximity to customers reduced latency
- Available services within a Region: new services and new features aren’t available in every Region
- Pricing – different service have different pricing
AWS Availability Zones
What is it -A Global Infrastructure which is composed of one or more discrete data centers with redundant power, networking, and connectivity, and are used to deploy infrastructure.
- Each region has many availability zones (usually 3, min is 2, max is 6).
- Each availability zone (AZ) is one or more discrete data centers with redundant power, networking, and connectivity
- They’re separate from each other, so that they’re isolated from disasters
AWS Points of Presence (Edge Locations)
It is a site in order to facilitate Content is delivered to end users with lower latency
AWS Services categories based on region
AWS has Global Services:
- Identity and Access Management (IAM)
- Route 53 (DNS service)
- CloudFront (Content Delivery Network)
- WAF (Web Application Firewall)
Most AWS services are Region-scoped:
- Amazon EC2 (Infrastructure as a Service)
- Elastic Beanstalk (Platform as a Service)
- Lambda (Function as a Service)
- Rekognition (Software as a Service)
Shared Responsibility Model diagram
What is it? Security and Compliance is a shared responsibility between AWS and the customer.
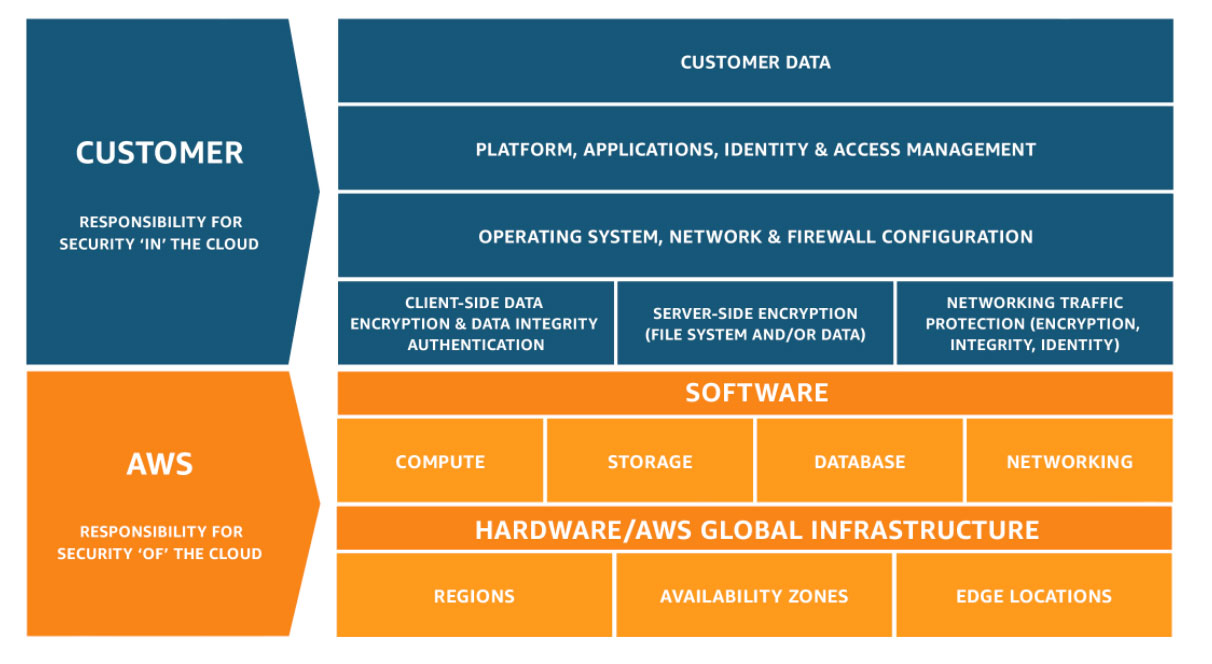
AWS responsibility “Security of the Cloud” – AWS is responsible for protecting the infrastructure that runs all of the services offered in the AWS Cloud. This infrastructure is composed of the hardware, software, networking, and facilities that run AWS Cloud services.
Customer responsibility “Security in the Cloud” – Customer responsibility will be determined by the AWS Cloud services that a customer selects. This determines the amount of configuration work the customer must perform as part of their security responsibilities. For example, a service such as Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) is categorized as Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) and, as such, requires the customer to perform all of the necessary security configuration and management tasks.
The following exercises can help customers in determining the distribution of responsibility based on specific use case:
- To determine external and internal security and related compliance requirement use Industry frameworks like the NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF) and ISO
- To plan and execute your digital transformation at scale – CAF (Cloud Adoption Framework) and Well architect-ed best practices by AWS
- Digital catalog with thousands of software listings from independent software vendors that enable you to find, test, buy, and deploy software that runs on AWS. AWS Market place
- To evaluate the implementation of best practices for security, reliability, and performance – Well Architected Review
REf: https://aws.amazon.com/compliance/shared-responsibility-model/
AWS Acceptable Use Policy
What is it? This Acceptable Use Policy (“Policy”) governs your use of the services offered by Amazon Web Services,
What it ensures
- No Illegal, Harmful, or Offensive Use or Content
- No Security Violations
- No Network Abuse