7.Database & Analytics
Index
- Intro
- RDS – MySQL, Aurora
- Difference in-between types of RDS(Performance and Cost)
- ElasticCache -Memcache, Redis
- DynamoDB,DAX
- DAX vs ElasticCache
- RedShift -Columnar data
- amazon EMR
- Athena –
- Amazon QuickSight
- DocumentDB
- Neptune
- QLDB
Databases Intro
• Storing data on disk (EFS, EBS, EC2 Instance Store, S3) can have its limits
• Sometimes, you want to store data in a database…
• You can structure the data
• You build indexes to efficiently query / search through the data
• You define relationships between your datasets
• Databases are optimized for a purpose and come with different
features, shapes and constraints
NoSQL Databases
Benefits:
• Flexibility: easy to evolve data model
• Scalability: designed to scale-out by using distributed clusters
• High-performance: optimized for a specific data model
• Highly functional: types optimized for the data model
Examples: Key-value, document, graph, in-memory, search databases
Databases & Shared Responsibility on AWS
AWS offers use to manage different databases
- Benefits include:
- • Quick Provisioning, High Availability, Vertical and Horizontal Scaling
- • Automated Backup & Restore, Operations, Upgrades
- • Operating System Patching is handled by AWS
- • Monitoring, alerting
Note: many databases technologies could be run on EC2, but you must
handle yourself the resiliency, backup, patching, high availability, fault
tolerance, scaling…
AWS RDS Overview
RDS stands for Relational Database Service. It’s a managed DB service for DB use SQL as a query language
It allows you to create databases in the cloud that are managed by AWS
- Postgres
- MySQL
- MariaDB
- Oracle
- Microsoft SQL Server
- Aurora (AWS Proprietary database)
Advantage over using RDS versus deploying DB on EC2
- RDS is a managed service:
- Automated provisioning, OS patching
- Continuous backups and restore to specific timestamp (Point in Time Restore)!
- Monitoring dashboards
- Read replicas for improved read performance
- Multi AZ setup for DR (Disaster Recovery)
- Maintenance windows for upgrades
- Scaling capability (vertical and horizontal)
- Storage backed by EBS (gp2 or io1)
BUT you can’t SSH into your instances

Amazon Aurora – Aurora is a proprietary technology from AWS (not open sourced)
PostgreSQL and MySQL are both supported as Aurora DB
Aurora is “AWS cloud optimized” and claims 5x performance improvement
over MySQL on RDS, over 3x the performance of Postgres on RDS
• Aurora storage automatically grows in increments of 10GB, up to 64 TB.
• Aurora costs more than RDS (20% more) – but is more efficient
• Not in the free tier
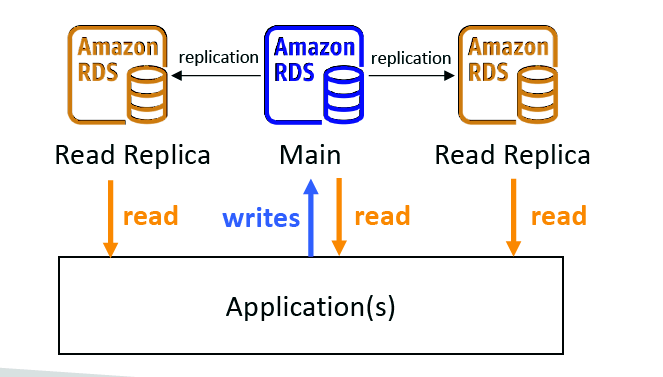
RDS Deployments: Read Replicas, Multi-AZ
Read Replicas: Replicas for read requests
• Scale the read workload of your DB
• Can create up to 5 Read Replicas
• Data is only written to the main DB
Multi-AZ:
- • Failover in case of AZ outage (high availability)
- Can only have 1 other AZ as failover
RDS Deployments: Multi-Region
Multi-Region (Read Replicas)
• Disaster recovery in case of region issue
• Local performance for global reads
• Replication cost

Amazon ElastiCache Overview
The same way RDS is to get managed Relational Databases…
• ElastiCache is to get managed Redis or Memcached
• Caches are in-memory databases with high performance, low latency
• Helps reduce load off databases for read intensive workloads
AWS takes care of OS maintenance / patching, optimizations, setup,
configuration, monitoring, failure recovery and backups
DynamoDB
- • Fully Managed Highly available with replication across 3 AZ
- • NoSQL database – not a relational database
- • Scales to massive workloads, distributed “serverless” database
- • Millions of requests per seconds, trillions of row, 100s of TB of storage
- • Fast and consistent in performance
- • Single-digit millisecond latency – low latency retrieval
- • Integrated with IAM for security, authorization and administration
- • Low cost and auto scaling capabilities
DynamoDB – type of data – DynamoDB is a key/value database
DynamoDB Accelerator – DAX
- Fully Managed in-memory cache for DynamoDB
- 10x performance improvement – single digit millisecond latency to microseconds latency – when accessing your DynamoDB tables
- Secure, highly scalable & highly available
- Difference with ElastiCache at the CCP (Cloud Practitioner) level: DAX is only used for and is integrated with DynamoDB, while ElastiCache can be used for other databases
Redshift Overview
- Redshift is based on PostgreSQL, but it’s not used for OLTP
- • It’s OLAP – online analytical processing (analytics and data warehousing)
- • Load data once every hour, not every second
- • 10x better performance than other data warehouses, scale to PBs of data
- • Columnar storage of data (instead of row based)
- • Massively Parallel Query Execution (MPP), highly available
- • Pay as you go based on the instances provisioned
- • Has a SQL interface for performing the queries
- • BI tools such as AWS Quicksight or Tableau integrate with it
Amazon EMR
- EMR stands for “Elastic MapReduce”
- Managed Hadoop framework
- EMR helps creating Hadoop clusters (Big Data) to analyze and process vast amount of data
- The clusters can be made of hundreds of EC2 instances
- Also supports Apache Spark, HBase, Presto, Flink…
- EMR takes care of all the provisioning and configuration
- Auto-scaling and integrated with Spot instances
- Use cases: data processing, machine learning, web indexing, big data…
Athena Overview
- Fully Serverless database with SQL capabilities
- Used to query data in S3
- Pay per query
- Output results back to S3
- Secured through IAM
Use Case: one-time SQL queries, serverless queries on S3, log analytics
Amazon QuickSight
Serverless machine learning-powered business intelligence service to
create interactive dashboards
- Fast, automatically scalable, embeddable, with per-session pricing
- Use cases:
- • Business analytics
- • Building visualizations
- • Perform ad-hoc analysis
- • Get business insights using data
Integrated with RDS, Aurora, Athena, Redshift, S3…
DocumentDB
- Aurora is an “AWS-implementation” of PostgreSQL / MySQL …
- DocumentDB is the same for MongoDB (which is a NoSQL database
MongoDB is used to store, query, and index JSON data
• Similar “deployment concepts” as Aurora
• Fully Managed, highly available with replication across 3 AZ
• Aurora storage automatically grows in increments of 10GB, up to 64 TB
Automatically scales to workloads with millions of requests per seconds
Amazon Neptune
Fully managed graph database
A popular graph dataset would be a social network
- • Users have friends
- • Posts have comments
- • Comments have likes from users
- • Users share and like posts…
Amazon QLDB
- QLDB stands for ”Quantum Ledger Database”
- A ledger is a book recording financial transactions
- Fully Managed, Serverless, High available, Replication across 3 AZ
- Used to review history of all the changes made to your application data over time
- Immutable system: no entry can be removed or modified, cryptographically verifiable
- 2-3x better performance than common ledger blockchain frameworks, manipulate data using SQL
- Difference with Amazon Managed Blockchain: no decentralization (it’s centralized )component, in accordance with financial regulation rules
Amazon Managed Blockchain
- Blockchain makes it possible to build applications where multiple parties can execute transactions without the need for a trusted, central authority.
Amazon Managed Blockchain is a managed service to:
• Join public blockchain networks
• Or create your own scalable private network
Compatible with the frameworks Hyperledger Fabric & Ethereum
AWS Glue
- Managed extract, transform, and load (ETL) service
- Fully serverless service
DMS – Database Migration Service
• Quickly and securely migrate databases to AWS, resilient, self healing
• The source database remains available during the migration
Supports:
• Homogeneous migrations: ex Oracle to Oracle
• Heterogeneous migrations: ex Microsoft SQL Server to Aurora