8.Other Compute Section
Index
- Docker
- ECS
- Fargate
- ECR
- Why Lambda?
- AWS API Gateway
- aws Batch
- lambda vs Batch
- Light sail
What is Docker?
- Docker is a software development platform to deploy apps,
- Apps are packaged in containers that can be run on any OS
- Apps run the same, regardless of where they’re run
- Any machine
- No compatibility issues
- Predictable behavior
- Scale containers up and down very quickly (seconds)
Where Docker images are stored?
Docker images are stored in Docker Repositories
Public: Docker Hub https://hub.docker.com/
• Find base images for many technologies or OS:
• Ubuntu
• MySQL
• NodeJS, Java…
Private: Amazon ECR (Elastic Container Registry) [in layman terms – its kind of source code/image storing aws managed service]
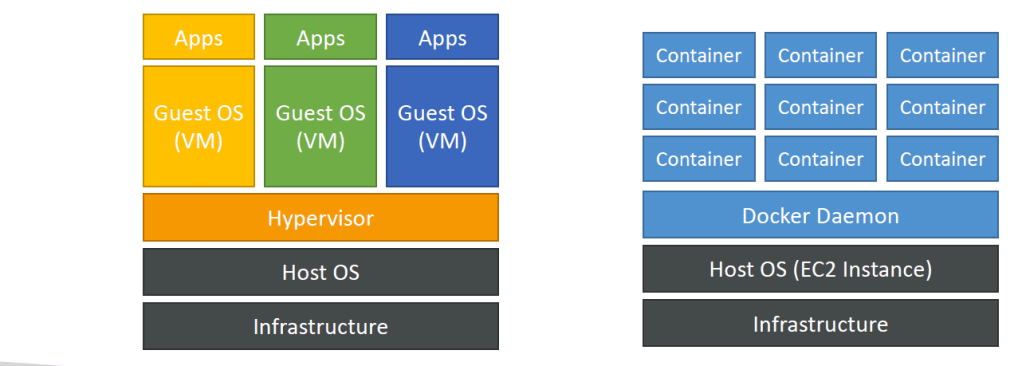
Docker versus Virtual Machines
In Docker Resources are shared with the host => many containers on one server
ECS
ECS = Elastic Container Service
Launch Docker containers on AWS
• You must provision & maintain the infrastructure (the EC2 instances)
• AWS takes care of starting / stopping containers
• Has integrations with the Application Load Balancer
Fargate – [Mind-map – abstraction over ECS]
• Launch Docker containers on AWS
• You do not provision the infrastructure (no EC2 instances
to manage) – simpler!
• Serverless offering
• AWS just runs containers for you based on the CPU / RAM you need
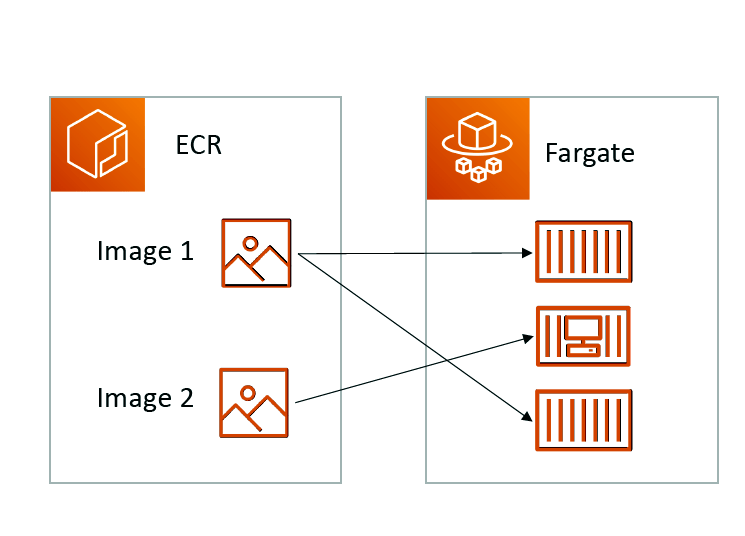
ECR
• Elastic Container Registry
• Private Docker Registry on AWS
• This is where you store your Docker images so they can be run by ECS or Fargate
What’s serverless?
• Serverless is a new paradigm in which the developers don’t have to manage servers anymore…
• They just deploy code
• They just deploy… functions !
• Initially… Serverless == FaaS (Function as a Service)
• Serverless was pioneered by AWS Lambda but now also includes anything that’s managed: “databases, messaging, storage, etc.”
• Serverless does not mean there are no servers…
it means you just don’t manage / provision / see them
Why AWS Lambda?
Shortcoming of EC2
- Virtual Servers in the Cloud
- Limited by RAM and CPU
- Continuously running
- Scaling means intervention to add / remove servers
Lambda Working –
- Virtual functions – no servers to manage!
- Limited by time – short executions
- Run on-demand
- Scaling is automated
Benefits of AWS Lambda
- Easy Pricing:
- Pay per request and compute time
- Free tier of 1,000,000 (i.e 1M) AWS Lambda requests and 400,000 GBs of compute time
- Integrated with the whole AWS suite of services
- Event–Driven: functions get invoked by AWS when needed
- Integrated with many programming languages
- Easy monitoring through AWS CloudWatch
- Easy to get more resources per functions (up to 10GB of RAM!)
- Increasing RAM will also improve CPU and network!
Example: Serverless CRON Job

AWS Lambda Pricing: example
- Pay per calls:
- First 1,000,000 requests are free
- $0.20 per 1 million requests thereafter ($0.0000002 per request)
- Pay per duration: (in increment of 1 ms)
- 400,000 GB-seconds of compute time per month for FREE
- == 400,000 seconds if function is 1GB RAM
- == 3,200,000 seconds if function is 128 MB RAM
- After that $1.00 for 600,000 GB-seconds
- It is usually very cheap to run AWS Lambda so it’s very popular
Amazon API Gateway
- Fully managed service for developers to easily create, publish, maintain, monitor,and secure APIs
- Serverless and scalable
- Supports RESTful APIs and WebSocket APIs
- Support for security, user authentication, API throttling, API keys, monitoring…
AWS Batch
- • Fully managed batch processing at any scale
- • Efficiently run 100,000s of computing batch jobs on AWS
- • A “batch” job is a job with a start and an end (opposed to continuous)
- • Batch will dynamically launch EC2 instances or Spot Instances
- • AWS Batch provisions the right amount of compute / memory
- • You submit or schedule batch jobs and AWS Batch does the rest!
- • Batch jobs are defined as Docker images and run on ECS
- • Helpful for cost optimizations and focusing less on the infrastructure
Batch vs Lambda
Lambda:
• Time limit
• Limited runtimes
• Limited temporary disk space
• Serverless
Batch:
• No time limit
• Any runtime as long as it’s packaged as a Docker image
• Rely on EBS / instance store for disk space
• Relies on EC2 (can be managed by AWS)
Amazon Lightsail
- Virtual servers, storage, databases, and networking
- Low & predictable pricing
- Simpler alternative to using EC2, RDS, ELB, EBS, Route 53…
- Great for people with little cloud experience!
- Can setup notifications and monitoring of your Lightsail resources
- Use cases:
- Simple web applications (has templates for LAMP, Nginx, MEAN, Node.js…)
- Websites (templates for WordPress, Magento, Plesk, Joomla)
- Dev / Test environment
- Has high availability but no auto-scaling, limited AWS integrations
Lambda Summary
- • Lambda is Serverless, Function as a Service, seamless scaling, reactive
- • Lambda Billing:
- • By the time run x by the RAM provisioned
- • By the number of invocations
- • Language Support: many programming languages except (arbitrary) Docker
- • Invocation time: up to 15 minutes
- • Use cases:
- • Create Thumbnails for images uploaded onto S3
- • Run a Serverless cron job
- • API Gateway: expose Lambda functions as HTTP API