Index-
- Single Linked List
- Define the Structure and add element
- traversal
- Find loop
- Reverse link-list
- Mid element
- Delete duplicate
- Doubly Linked-list
- DLL introduction and representation
- Advantages and Disadvantages
- Adding the Nodes
- at end
- at begging
- after a given node
- before a given node
1.Define the Structure and add element
//Structure and insertion
//Step-1 - Declare a Node class (preferably in same package same class as private member)
//Step-2 : linkledlist implementation class and corresponding methods in it
public class MyLinkedListImpl<E> {
private class Node<E> {
E key;
Node<E> next;
Node(E key) { //constructor with parameter of value only and next always null
this.key = key;
this.next = null;
}
}
//must have the head of linklist as a node
static Node<Integer> head;
static MyLinkedListImpl linkedL = new MyLinkedListImpl();
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*hard-coding the node values*/
// linkedL.head=new Node<Integer>(1);
//linkedL.head.next=new Node<Integer>(2);
/*by standard process*/
append(5);
append(4);
/*for traversig the nodes -call method wtih head send as parameter*/
linkedL.printNode(head);
/*finding the loop*/
boolean hasLoop = linkedL.findaLoop();
/*way to introduce a loop*/
// linkedL.head.next.next.next.next = linkedL.head;
head = reverseLinkedList(head);
// System.out.println("lop: " + hasLoop);
}
//Insert node at end of linked-list
private static void append(int i) {
//Step1- create a new object of node to store new node data
Node<Integer> n1 = new Node<Integer>(i);
//if the linklist is empty then insert at top
if (linkedL.head == null) {
linkedL.head = n1;
} else {
//traverse till next of node is null and link the node (simple assignment)
Node<Integer> n = linkedL.head;
while (n.next != null) {
n = n.next;
}
n.next = n1;
}
}
- In above code block, methods to insert a new node in linked list are discussed. A node can be added in three ways
- 1) At the front of the linked list
- 2) After a given node.
- 3) At the end of the linked list. (above method)
//insert afrer a node
private static boolean insertAfter(Node<Integer> afterNode, int j) {
boolean result = false;
if (linkedL.head == null)
return result;
else if (afterNode.next == null) {
Node<Integer> newNode = new Node<Integer>(j);
afterNode.next = newNode;
result = true;
} else {
Node<Integer> newNode = new Node<Integer>(j);
newNode.next = afterNode.next;
afterNode.next = newNode;
result = true;
}
return result;
}
//Insert at beginning
/**
* @param value Check Condition for if root element id null simple 4 step
*/
private static void push(int value) {
Node<Integer> n1 = new Node<Integer>(value);
n1.next = linkedL.head;
linkedL.head = n1;
// return linkedL;
}
2.Traverse
//Traverse
private void printNode(Node<Integer> head) {
Node<Integer> node = head;
while (node != null) {
System.out.print(node.key + "--> ");
node = node.next;
}
System.out.println("");
}
3.Find Loop/Cycle
//Loop
/**
* @return Fischer cycle way
*/
private boolean findaLoop() {
boolean result = false;
Node<Integer> p1 = linkedL.head;
Node<Integer> p2 = linkedL.head;
while (p1 != null && p2 != null && p2.next != null) {
p1 = p1.next;
p2 = p2.next.next;
if (p1 == p2) {// note key are not compared the node itself is compared
result = true;
break;
}
}
return result;
}
4.Reverse the Linked-list
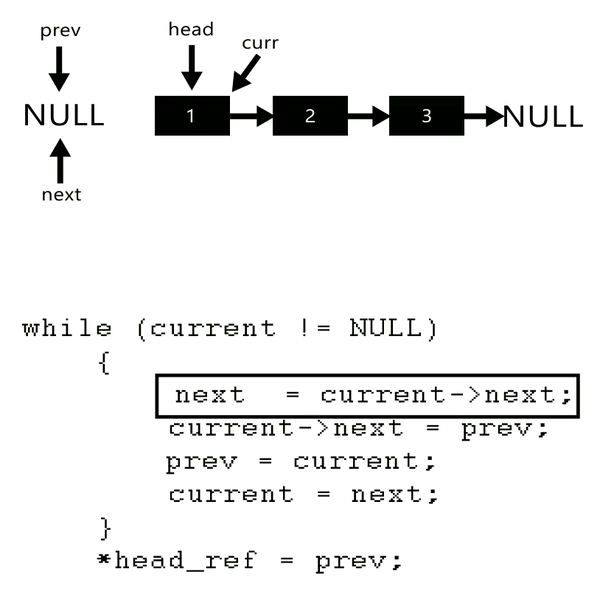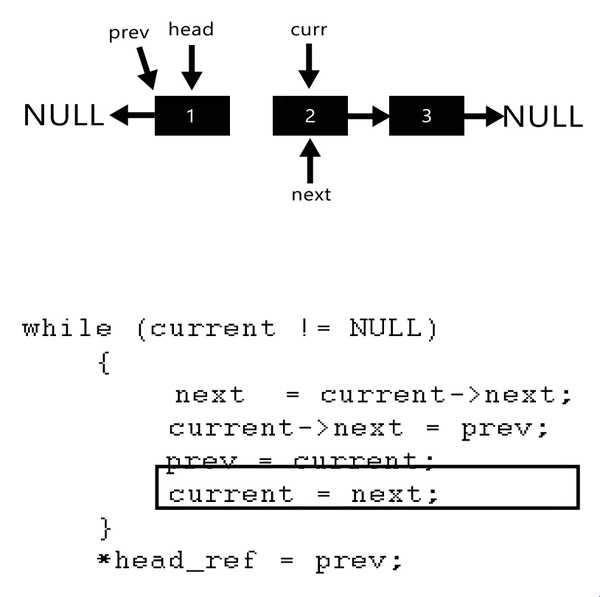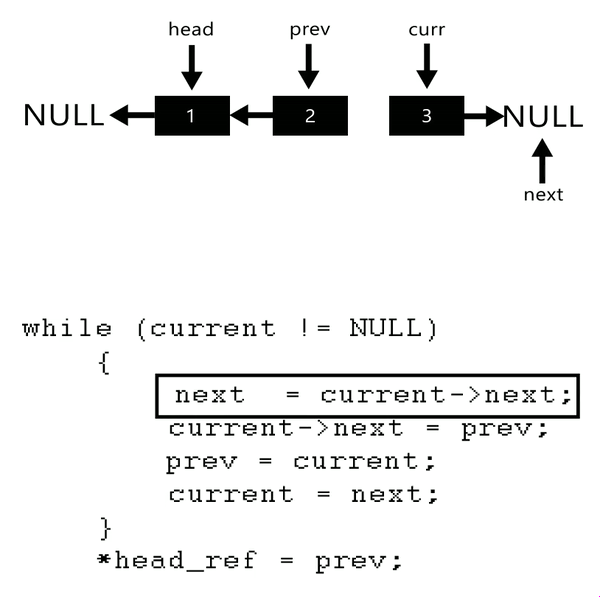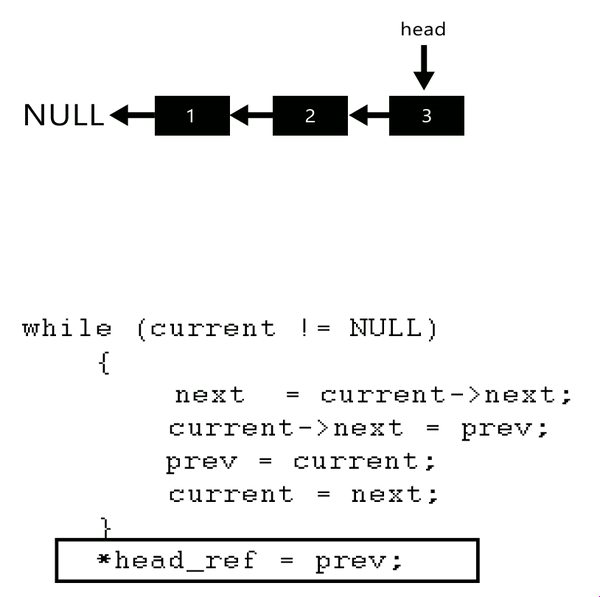
- Algorithm
- Initialize three pointers prev as NULL, curr as head and next as NULL.
- Iterate through the linked list. In loop, do following.
- / Before changing next of current,
- // store next node
- next = curr->next
- // Now change next of current
- // This is where actual reversing happens
- curr->next = prev
- // Move prev and curr one step forward
- prev = curr
- curr = next
//Reverse
private static Node reverseLinkedList(Node head) {// problen us no link in btw
Node current = head;
Node next = null;
Node prev = null;
while (current != null) {// not next current checked so as to assign all link
// change the linking
next = current.next;
current.next = prev;
// move a step ahead
prev = current;
current = next;
}
/*prev is return ed as it pointed head after reversal*/
return prev;
}
5.Palindrom
//PAlindrom
REcursice way
passs two SB one dring passing and one build while unwinding if bith equal then palindrome
https://www.techiedelight.com/recursively-check-linked-list-characters-palindrome-or-not
6.Center Element
//Loop
Remove Duplicate
public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) {
HashSet hs=new HashSet<>();
ListNode h=head,prev=null;
while(h!=null){
if(hs.add(h.val)){
prev=h;
}else{
prev.next=h.next;
}
h=h.next;
}
return head;
}