Index:
- Introduction & Representation techniques
- OOAD (Object Oriented Analysis and Design) – CDAC reference
- Representation using UML(Unified Modelling Language) notation
- For Drawing UML Tools-
- Offline- StarUML,
- Online – Diagrams.net
- OO Analysis and Design Methodolgy
- OO Notation
- OO tool to draw OOAD Design
- OOAD (Object Oriented Analysis and Design) – CDAC reference
- OOP (implementation)
- OOP Principal
- P.I.E.A.
- SOLID
- Association, Aggregation, Composition
- OOP Principal
- Design pattern (implementation)
- Behavioural
- Creational
- Structural
- Interview Outline
What does a OO Designer needs?
- OO Concepts
- OO Language
- OO Analysis and Design Methodolgy
- OO Notation
- OO tool to draw OOAD Design
OOAD Techniques
- Fusion
- Jacobson
- Rumbaugh
- Booch
- Rational Unified Process (RUP) with Unified Modeling Language (UML)
OO Design Tools
- Rational Software
- StarUML
UML Diagrams for OOAD design using RUP
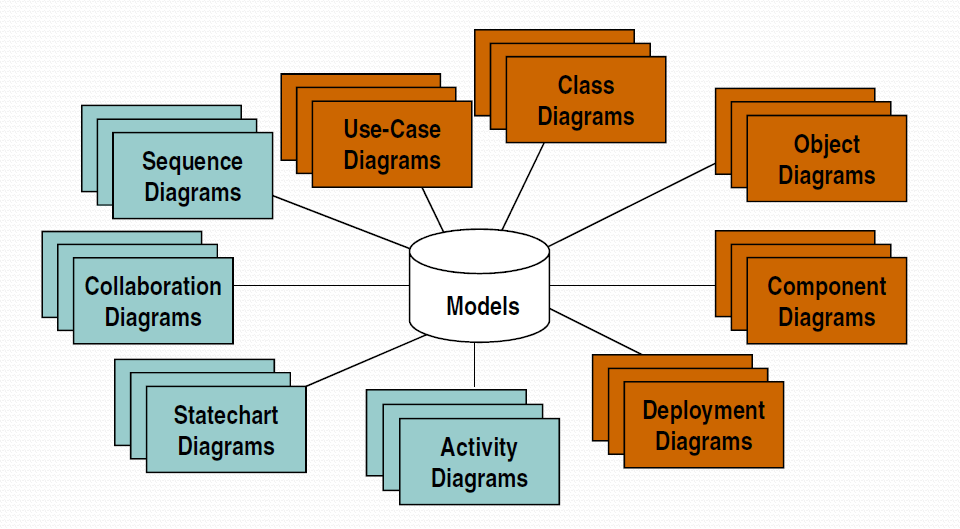
At core we have Models and using which various representation can be drawn for specific analysis-
- Use-case Diagrams
- Class Diagrams
- Object Diagrams
- State-chart Diagrams
- Sequence Diagrams
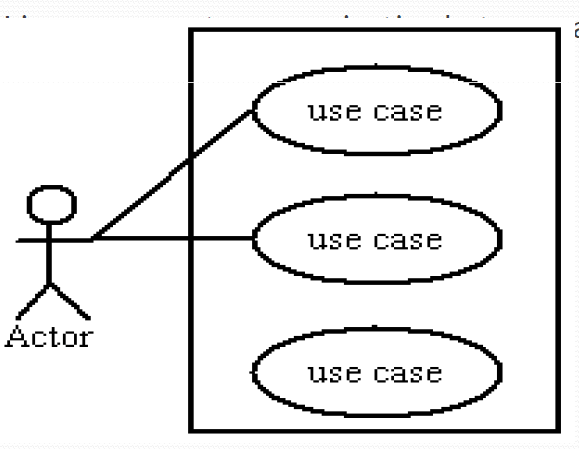
Use Case Analysis – Drawing the Use Case Diagram
My take- useful in case of establishing relation between use-case/functionality
- Stick Figure Represents Actor
- Oval Represents Use Case
- The Rectangle represents System Boundary
Use Case Analysis – Use Case Relationships
3 kinds of relationships between use cases
- Include
- Extend
- Uses
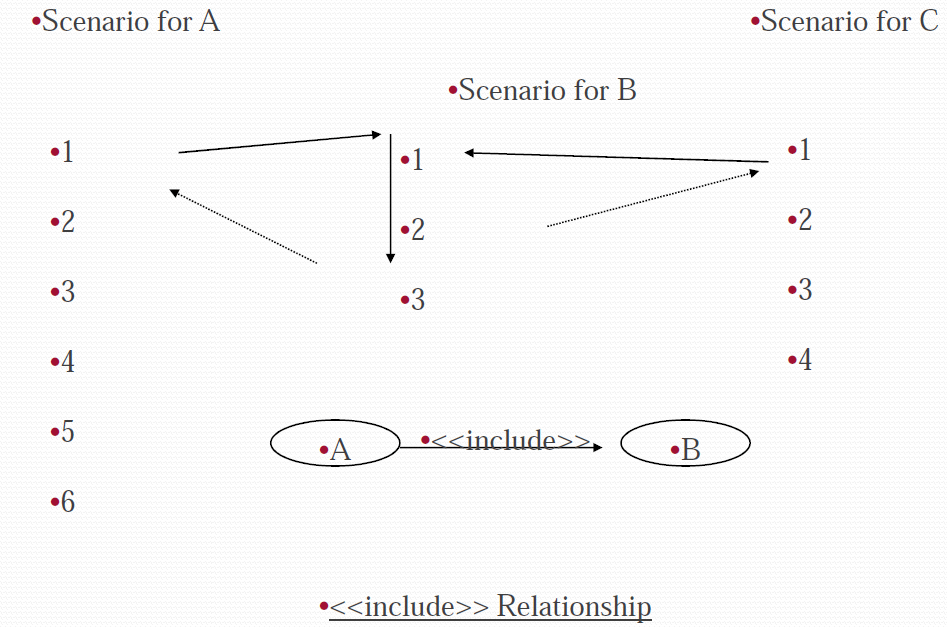
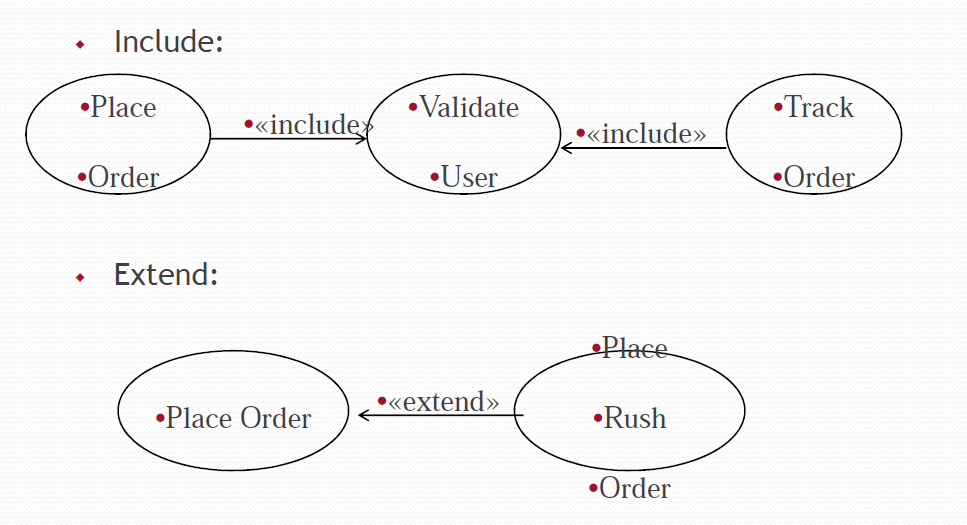
Include:
- «include» stereotype indicates that one use case “includes” the contents of another use case.
- Enables factoring out frequent common behavior
Use case “A” includes use case “B” if :
- B describes scenario which is part of scenario of A &
- B describes scenario common for a set of use cases including A
Extends:
- «extend» stereotype indicates that one use case is “extended” by another use case.
- Enables factoring out infrequent behavior or error conditions
- Used to show optional behaviour for a use case which will be required only under certain conditions
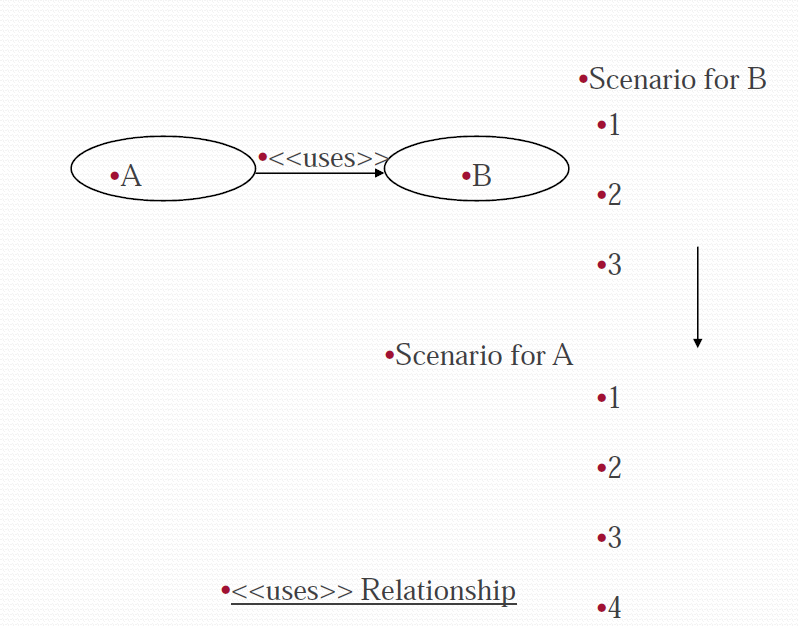
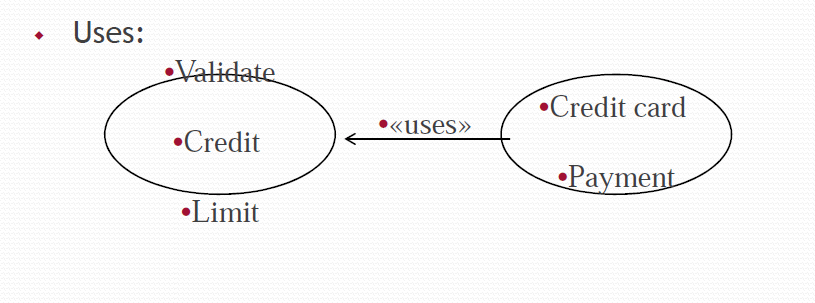
Uses:
- «uses» stereotype indicates that one use case is precondition for executing another use case
- Use case “A” uses use case “B” if
- B describes a scenario which is not part of scenarios carrying out service A &
- B is a precondition for successful invocation of A
Examples
OOAD: Activity Diagram
Depicts business processes and data flows to model the complex logic within the system
OOAD: Sequence Diagrams
Models the time ordering of messages between classifiers to accomplish given
functionality
UML Diagrams: Collaboration Diagrams
Focuses on the structural organisation of objects that send and receive messages.
Known as communication diagrams in UML 2.0.
UML Diagrams: Class Diagrams
Models a collection of static model elements such as classes, their contents and
relationships
UML Diagrams: State machine Diagrams
Describes states of an object and transitions between the states
UML Diagrams: Component Diagrams
Depicts the components, their interfaces and interrelationships
UML Diagrams: Deployment Diagrams
Shows the execution architecture of the application