Creational Design pattern
These design patterns provide a way to create objects while hiding the creation logic, rather than instantiating objects directly using new operator. This gives more flexibility to the program in deciding which objects need to be created for a given use case.
PATTERNS COVERED –
- Singleton Design Pattern
- Builder Design Pattern
- Factory Method
- Abstract factory
- Prototype
- Object Pool
Ab – Creational has singleton so –Single .Building. Ab. Factory Prototype. hai
SINGLETON DESIGN PATTERN
What is it?
Ensure a class only has one instance, and provide a global point of access to it.
When to use it? – Use in case
- There must be exactly one instance of a class, and it must be accessible to clients from a well-known access point.
How to achieve it?
Code for singleton class creation : Creational Design pattern repository link
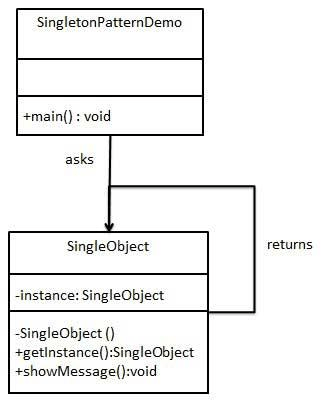
This pattern involves a single class(e.g SingleObject) which is responsible to create an object while making sure that only single object gets created. This class provides a way to access its only object which can be accessed directly without instantiating the
object of the class.
Structure
Implementation
Step 1
Create a Singleton Class.
Step 2
Get the only object from the singleton class.
How to verify if only a single object is created?
In Java if the two objects are same then, their hash key have to be equal. Let’s test that. If the above Singleton is correctly implemented than below code should return the same hash key.
IMPLEMENTATION COMPLEXITY
problem1 – Eager initialization method has one drawback. Here instance is created even though client application might not be using it. This might be a considerable issue if your Singleton class in creating a database.
Solution Lazy Initialization:
Problem 2- Reflection accessibility : In above Singleton class, by using reflection you can create more than one instance. Java Reflection is a process of examining or modifying the run-time behavior of a class at run time.
You can make the new instance of the Singleton class by changing the constructor visibility as public in run-time and create new instance using that constructor. below code will break the singleton property.
solution : To prevent Singleton failure while due to reflection you have to throw a run-time exception in constructor, if the constructor is already initialized and some class to initialize it again. Let’s update SingleObject.java.
problem 3 – thread safety – If two threads try to initialize the Singleton class at almost the same time, below code in which two threads are created almost simultaneously and they are calling getInstance().
If you run this code many times, you will see sometimes both the threads creates different instances.
Solution 1 : make the method getInstance() synchronized
As you made your getInstance() class synchronized the second thread will have to wait until the getInstance() method is completed for the first thread. This way we can achieve thread safety.
But, there are some cons of using this approach:
- Slow performance because of locking overhead.
- Unnecessary synchronization that is not required once the instance variable is initialized.
Solution 2. Double check locking method:
You can overcome this issue if you use Double check locking method to create the Singleton.
In this, you will make the Singleton class in the synchronized block if the instance is null. So, the synchronized block will be executed only when the instance is null and prevent unnecessary synchronization once the instance variable is initialized
Solution 3 – Use volatile keyword:
Without volatile modifier, it’s possible for another thread in Java to see half initialized state of instance variable, but with volatile variable guaranteeing happens-before relationship, all the write will happen on volatile instance before any read of instance variable.
problem 4 – New object creation while Serialization/Deserialization
Sometimes in distributed systems, you need to implement Serializable interface in Singleton class. By doing that you can store its state in the file system and retrieve it at later point of time.
The problem with above serialized singleton class is that whenever we deserialize it, it will create a new instance of the class.
Solution : To prevent creation of another instance you have to provide the implementation of readResolve() method. readResolve() replaces the object read from the stream. This ensures that nobody can create another instance by serializing and deserializing the singleton.
Standard Implementation in JDK –
Database connection
Interview Question – How to limit to 2 objects of a class
Sounds like you need multiple yet limited number of instances of a class. In that case, Object Pool pattern can be useful for you.
Example and usecase-
Java.land.Runtime calss is a singleton class instace we can get using Java.land.Runtime.getRuntime()
Verify singleton- every-time the hash-code will be same
Why Runtime is a singleton ?
Every Java application has a single instance of class Runtime that allows the application to interface with the environment in which the application is running. The current runtime can be obtained from the getRuntime() method.
An application cannot instantiate this class so multiple objects can’t be created for this class. Hence Runtime is a singleton class. [otherwise couldn’t interface correctly with environment different objects having different state]
BUILDER DESIGN PATTERN
FACTORY METHOD DESIGN PATTERN
In Factory pattern, we create object without exposing the creation logic to the client and refer to newly created object using a common interface.
Implementation
We’re going to create a Shape interface and concrete classes implementing the Shape interface. A factory class ShapeFactory is defined as a next step.
FactoryPatternDemo, our demo class will use ShapeFactory to get a Shape object. It will pass information (CIRCLE / RECTANGLE / SQUARE) to ShapeFactory to get the type of object it needs.

Step 1
Create an interface.
Shape.java
Step 2
Create concrete classes implementing the same interface.
Rectangle.java
Square.java
Circle.java
Step 3
Create a Factory to generate object of concrete class based on given information.
ShapeFactory.java
Step 4
Use the Factory to get object of concrete class by passing an information such as type.
FactoryPatternDemo.java
Question
- Why not use Auto-wiring instead of Factory pattern
PAGE BREAK
ABSTRACT FACTORY DESIGN PATTERN
Abstract Factory patterns work around a super-factory which creates other factories. This factory is also called as factory of factories. This type of design pattern comes under creational pattern as this pattern provides one of the best ways to create an object.
In Abstract Factory pattern an interface is responsible for creating a factory of related objects without explicitly specifying their classes. Each generated factory can give the objects as per the Factory pattern.
Implementation
We are going to create a Shape interface and a concrete class implementing it. We create an abstract factory class AbstractFactory as next step. Factory class ShapeFactory is defined, which extends AbstractFactory. A factory creator/generator class FactoryProducer is created.
AbstractFactoryPatternDemo, our demo class uses FactoryProducer to get a AbstractFactory object. It will pass information (CIRCLE / RECTANGLE / SQUARE for Shape) to AbstractFactory to get the type of object it needs.

Step 1
Create an interface for Shapes.
Shape.java
Step 2
Create concrete classes implementing the same interface.
RoundedRectangle.java
RoundedSquare.java
Rectangle.java
Step 3
Create an Abstract class to get factories for Normal and Rounded Shape Objects.
AbstractFactory.java
Step 4
Create Factory classes extending AbstractFactory to generate object of concrete class based on given information.
ShapeFactory.java
RoundedShapeFactory.java
Step 5
Create a Factory generator/producer class to get factories by passing an information such as Shape
FactoryProducer.java
Step 6
Use the FactoryProducer to get AbstractFactory in order to get factories of concrete classes by passing an information such as type.
AbstractFactoryPatternDemo.java
PROTOTYPE DESIGN PATTERN