Index
- var keyword – for local variable representation
- use if var keyword in lambdas
- String class new method
- isEmpty()
- Files class new mwthod
- createDirectories(directory/hireacrchy/to/create)
- Nested class based access control
- HttpClient
Index
Index
Index
| Version | Release Date | Major Features | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3.2.3 | February 22, 2024 | Upgraded dependencies (Spring Framework 6.1.4, Spring Data JPA 3.1.3, Spring Security 6.2.2, etc.) https://www.codejava.net/spring-boot-tutorials | |
| 3.1.3 | September 20, 2023 | Enhanced developer experience, improved reactive support, and updated dependencies https://spring.io/blog/2022/05/24/preparing-for-spring-boot-3-0 | |
| 3.0.x | May 2020 – December 2022 | Introduced reactive programming, improved build system, and various dependency updates throughout the series (refer to official documentation for details) | |
| 2.x | March 2018 – May 2020 | Introduced Spring Boot actuator, developer tools, and auto-configuration (refer to official documentation for specific features within each version) | 2.7.7 used in project (switch) |
| 1.x | April 2014 – February 2018 | Initial versions focusing on simplifying Spring application development | 1.5.22.RELEASE used in project (consumers) |
Springboot versions and corresponding spring version support:
| Spring Boot Version | Supported Spring Framework Versions |
|---|---|
| 1.x | 4.x |
| 2.0.x – 2.3.x | 5.x |
| 2.4.x | 5.x, 6.x |
| 3.0.x – 3.2.x | 6.x |
@Service are automatically recognized and configured based on conventions.@Service annotated classes, Spring Boot will automatically configure them as Spring beans.INdex
Design patterns
INdex
Key Differences:
Active MQ vs IBM MQ / WebSphere MQ Vs Kafka
| Kafka | IBM MQ/ WebSphere MQ | ActiveMQ (Apache) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Use Case Focus | Distributed event streaming platform for handling real-time data streams. | Enterprise messaging system for reliable and secure communication. | General-purpose message broker for asynchronous communication. |
| Scalability | Built for horizontal scalability and high throughput. | Can be configured for high availability and clustering. | Can be horizontally scaled. |
| Message Persistence | Persists messages and provides fault-tolerant storage.(how?) | Emphasizes guaranteed delivery and transactional support. | Supports message persistence. |
| Programming Model | APIs available for multiple programming languages (Java, Scala, Python, etc.). | Supports multiple programming languages and platforms. | JMS-based, often used in Java applications. |
THere are number of standards that define protocols[rules] for transactions [be it financial or non financial – ]. these standards ecusre consistency in excahneg of information between difeernt entities envlolevd(bank[acquirer,issuer,]merchant,user) . e.g one of the stadnrd that is widely used internationally ISO20022[for all paymentISO 8583 [specicically for card payment]] ,others include ACH managed by ACHA
On similar line in india we have a payment standrd called UPI[Unified payment interface] manaed by NPCI[National Payment COrportatoin of INdia]
In UPI standrd of payment, it defines set of protocols in a specific forrmal[xml with header,body etc] used by invloded parties for transacation.
sample
<upi:phase>
<header> -- version </Header>
<Meta> type of phases</Meta>
<Txn> -txn details -C|D|CR|DR|R
<Rules>- primarily for mandates- for expiry time
</Txn>
<Payer namr""> -- payer details</Payer>
<Payee> - payee ddetails </payee>
</upi:phase>
Note: std structured as elements of xmls i.e root, childs i.e header,meta,txn,payer , payee etc. and elements have attributes e.g name in payer that add additional information .
Tranasction has different phases OR is managed by different APIs and
there are protocol related to each phases \APIs- reqpay,respay , req-auth,respauth, req-paycollect , reqpay-intent, reqpay-mandate, resp-paymandate []
above mentoined protocol are used with varitoues instruments[cards,lite-payment,FIR,wallet-transaction etc.] with variation in the parameters/atributes/elemnts passed as part of standed protocol.
We can go in more deplth of each phases as folllowops posts.
Index
Definition
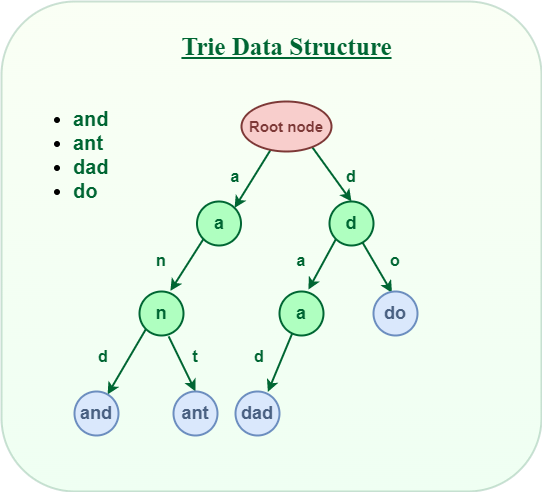
Time Complexity
Programmatic representation
class TrieNode{
//representing one of 26 characters of alphabet for a node
TrieNode children;
//representing last node of string.
boolean isLastNode;
TrieNode(){
children=new TrieNode[26];
isLastNode=false;
}
}
Trie Operation and applications:
Insertion :
class TrieNode{
TrieNode children;
boolean isLastNode;
TrieNode(){
children=new TrieNode[26];
isLastNode=false;
}
}
Class Trie{
TrieNode root;
Trie(){
root=new TrieNode();
}
public static void main(){
Trie trie=new Trie;
trie.insert("parag");
trie.insert("parameter");
trie.insert("parashoot");
trie.autocomplete("para");
}
private void insert(String word){
TrieNode current=root;
}
private void autoComplete(String prefix){
TrieNode current=root;
}
}
Application link and details :
Following are the parameters of Kafka that can be balanced one over other for performance-
Optimal Partition Configuration-
Increase the number of partitions. This will allow more consumers to read messages in parallel, which will improve throughput. so it the partition and consumer should have 1:1 ration for better performance?
Note: Kafka related Bottlenecks will not occur while pushing the data because as in this case it depends on external source of data how fast it generates. Bottlenecks occurs when huge data on topic and limited consumer capacity (instances, capacity, consumption configuration etc).
Use cases:
Case 1: If Kafka consumer is struggling to keep up with the incoming data (suppose 170million events data lag). To decrease the lag and improve the performance of your Kafka setup, you can consider the following steps:
fetch.min.bytes, fetch.max.wait.ms, max.poll.records, and max.partition.fetch.bytes settings to balance the trade-off between latency and throughput. Experiment with different values to find the optimal configuration for your use case.Index
API Docs:
For new features added in specific version of spring-kafka refer :
Notes to implement for performance:
https://spring.io/projects/spring-kafka#learn
linkedln :
13 ways to learn Kafka:
Kafka 3.1 features –
KafkaTemplate supporting CompletableFuture(?) instead of LIstenableFuture(?). References: https://docs.spring.io/spring-kafka/docs/current/reference/html/
Points :