Objectives
- Significance
- Flow of control
- Memory usage
- Interview FAQs
Recursion is a process by which a function or a method calls itself again and again. Analogy: Anything that can be done in for loop can be done by recursion
Iteration VS Recursion
| Criteria | Recursion | Iteration |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Recursion is a process where a method calls itself repeatedly until a base condition is met. | Iteration is a process by which a piece of code is repeatedly executed for a finite number of times or until a condition is met. |
| Applicability | Is the application for functions. | Is applicable for loops. |
| Chunk of code can be applied to? | Works well for smaller code size. | Works well for larger code size. |
| Memory Footprint | Utilizes more memory as each recursive call is pushed to the stack | Comparatively less memory is used. |
| Maintainability | Difficult to debug and maintain | Easier to debug and maintain |
| Type of errors expected | Results in stack overflow if the base condition is not specified or not reached | May execute infinitely but will ultimately stop execution with any memory errors |
| Time-Complexity | Time complexity is very high. | Time complexity is relatively on the lower side. |
Structure : Any method that implements Recursion has two basic parts:
- Method call which can call itself i.e. recursive
- A precondition that will stop the recursion.
Note that a precondition is necessary for any recursive method as, if we do not break the recursion then it will keep on running infinitely and result in a stack overflow.
Syntax- The general syntax of recursion is as follows:
methodName (T parameters…)
{
if (precondition == true)
//precondition or base condition
{
return result;
}
return methodName (T parameters…);
//recursive call
}
Associated Error – Stack Overflow Error In Recursion
We are aware that when any method or function is called, the state of the function is stored on the stack and is retrieved when the function returns. The stack is used for the recursive method as well.
But in the case of recursion, a problem might occur if we do not define the base condition or when the base condition is somehow not reached or executed. If this situation occurs then the stack overflow may arise.
Types of recursion
- Tail Recursion
- Head Recursion
- Tree recursion
Tail Recursion
When the call to the recursive method is the last statement executed inside the recursive method, it is called “Tail Recursion”.
In tail recursion, the recursive call statement is usually executed along with the return statement of the method.
methodName ( T parameters…){
{
if (base_condition == true)
{
return result;
}
return methodName (T parameters …) //tail recursion
}
Head Recursion
Head recursion is any recursive approach that is not a tail recursion. So even general recursion is ahead recursion.
methodName (T parameters…){
if (some_condition == true)
{
return methodName (T parameters…);
}
return result;
}
Tree Recursion
Has two recursive calls(Left/right sub-tree)
Problem-Solving Using Recursion
The basic idea behind using recursion is to express the bigger problem in terms of smaller problems. Also, we need to add one or more base conditions so that we can come out of recursion.
PAGE BREAK
FAQS
Q #1.How does Recursion work in Java?
Answer: In recursion, the recursive function calls itself repeatedly until a base condition is satisfied. The memory for the called function is pushed on to the stack at the top of the memory for the calling function. For each function call, a separate copy of local variables is made.
Q #2) Why is Recursion used?
Answer: Recursion is used to solve those problems that can be broken down into smaller ones and the entire problem can be expressed in terms of a smaller problem.
Recursion is also used for those problems that are too complex to be solved using an iterative approach. Besides the problems for which time complexity is not an issue, use recursion.
Q #3) What are the benefits of Recursion?
Answer:
The benefits of Recursion include:
- Recursion reduces redundant calling of function.
- Recursion allows us to solve problems easily when compared to the iterative approach.
Q #4) Which one is better – Recursion or Iteration?
Answer: Recursion makes repeated calls until the base function is reached. Thus there is a memory overhead as a memory for each function call is pushed on to the stack.
Iteration on the other hand does not have much memory overhead. Recursion execution is slower than the iterative approach. Recursion reduces the size of the code while the iterative approach makes the code large.
Recursion is better than the iterative approach for problems like the Tower of Hanoi, tree traversals, etc.
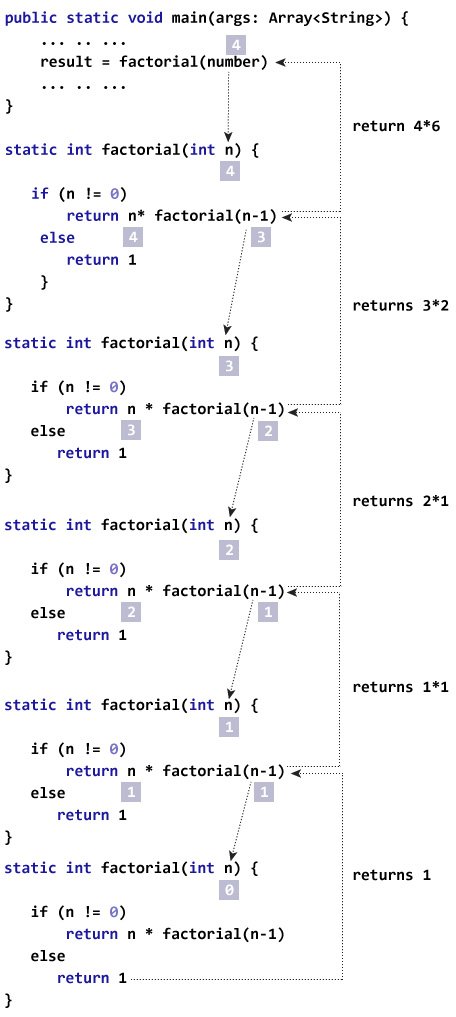
Question : how unflods while same method called:
https://leetcode.com/problems/merge-two-binary-trees/editorial/